Andesite
Category: Volcanic
Type Andesite, garnet-bearing.
Commons Andesite is an intermediate volcanic rock composed of zoned plagioclase (labrador An50-70 to oligoclase An10-30), pyroxene, hornblend and/or biotite. Magnetite, apatite, zircon and ilmenite are main accessory minerals. Some andesites contain also garnet phenocrysts. Andesite is volcanic equivalent of plutonic diorite.
Name origin Rock name is after Andes - the mountain chain extending along the western coast of the southern America.
Locality Šiatorská Bukovinka, Slovak Republic.
GPS: 48° 11' 23,3" N, 19° 49' 45,8" E
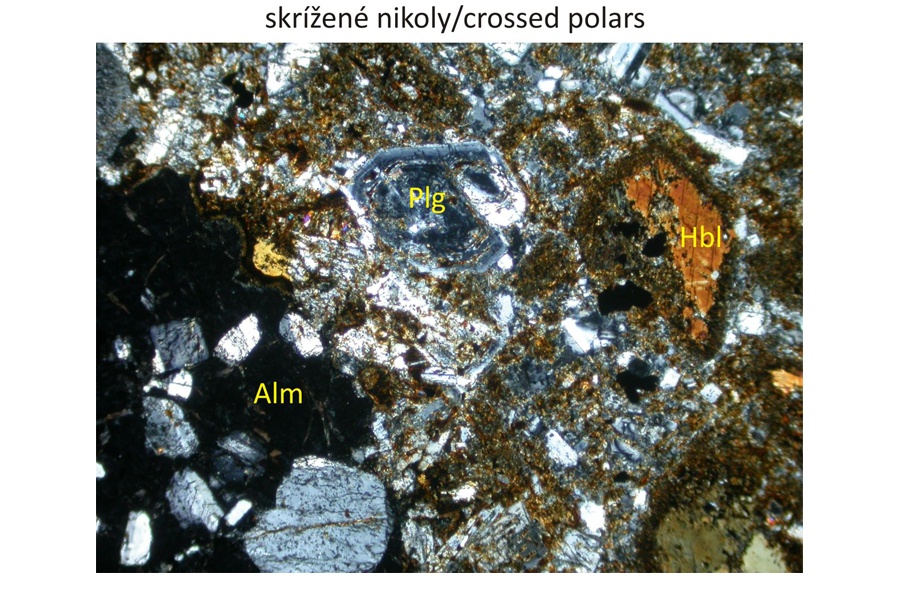
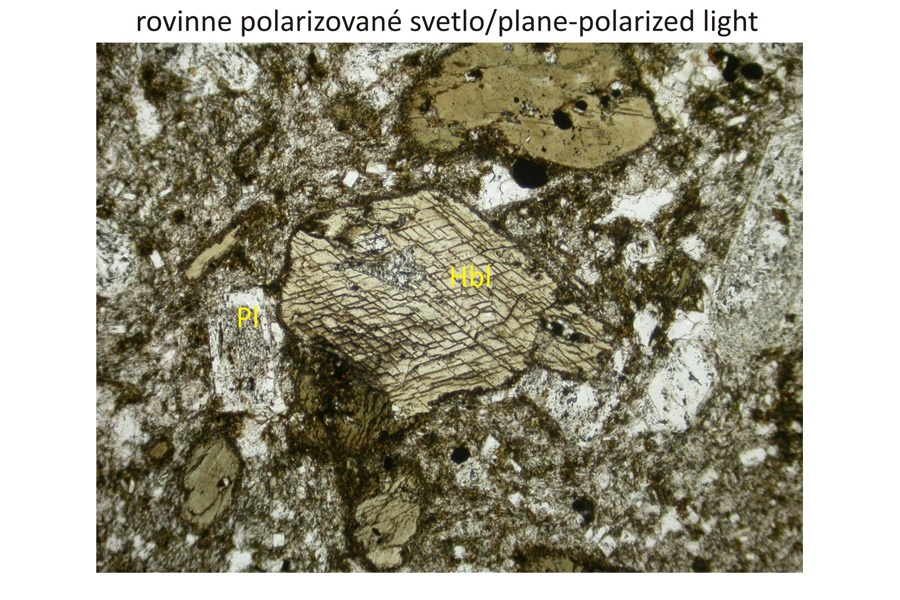
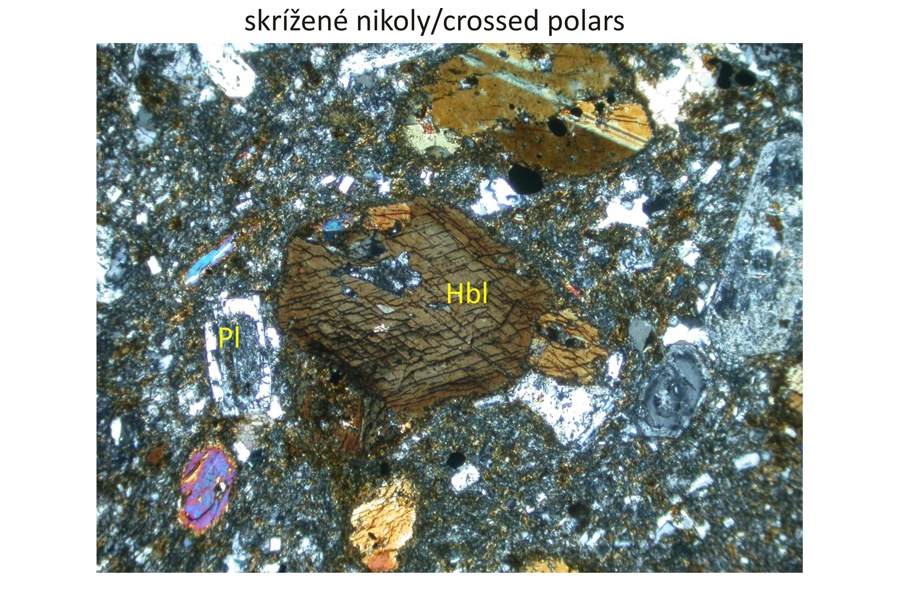
Major minerals Plagioclase (An41-88), hornblende, almandine.
Accessory minerals Ilmenite, apatite and orthopyroxene (En44-51Wo1-4Fs47-54).
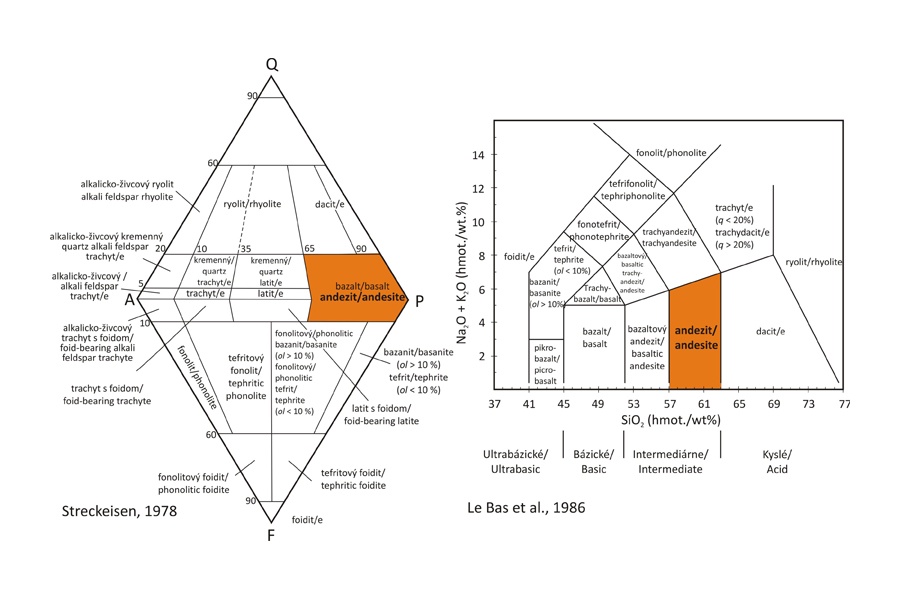
Classification According to modal composition projected within the QAPF discrimination diagram for volcanic rock (Streckeisen, 1978), the andesite project within basalt field. However, the andezit has higher SiO2 content (> 52 wt. %) compared to that in basalt with less than 52 wt. % SiO2.
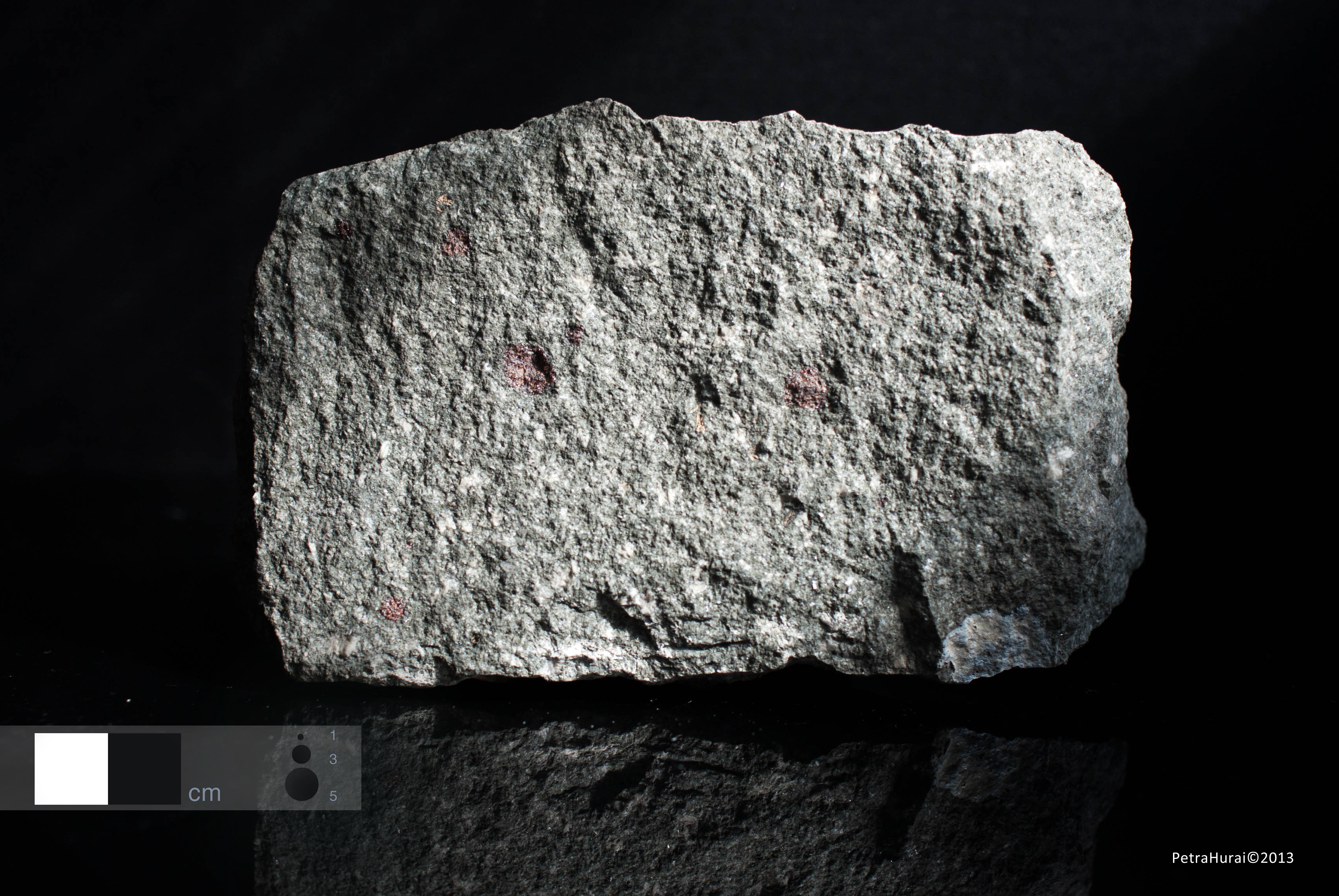

Colour Grey, greyish green.
Structure Compact.
Granularity Finely grained (0.1 - 1 mm).
Texture Aphanitic to porphyric with redish phenocrysts of garnet and plagioclase.
Alterations Plagioclases are in places transformed to clay minerals.
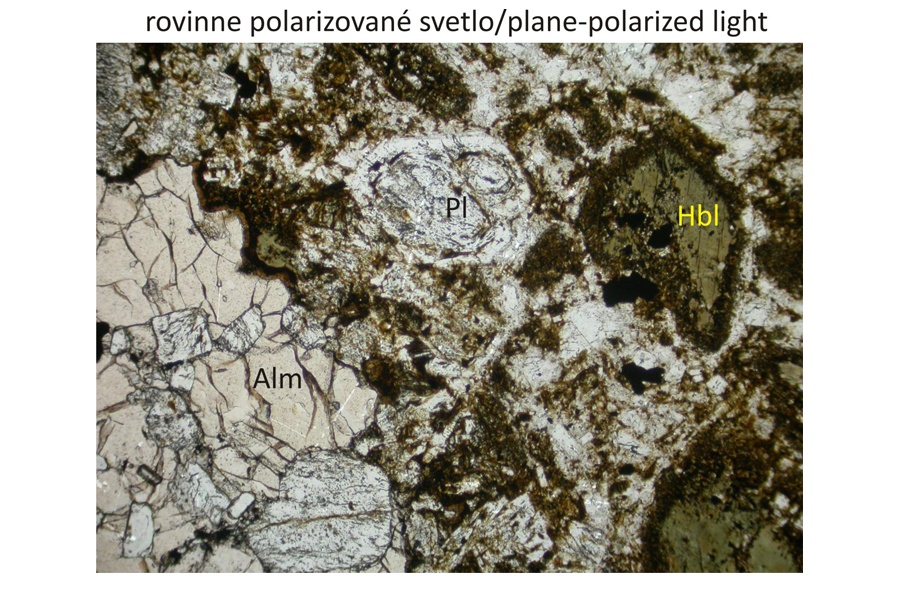
Petrographic characteristics The displayed specimen contains porphyric phenocrysts of almandine garnet coexisting with porphyric phenocrysts of plagioclase and hornblend. Orthopyroxene occurs as microphenocrysts. Matrix is dominated by plagioclases. Composite garnet phenocrysts belong to the type 3 (Harangi et al., 2001). They are composed of light-coloured xenocrystic core and magmatic rim. The garnet core contains ilmenite, biotite and orthopyroxene inclusions.
Usage Rock is used as a construction material.
Literature Harangi, Sz., Downes, H., Kósa, L., Szabó. Cs., Thirlwall, M.F., Mason, P.R.D & Mattey, D., 2001: Almandine Garnet in Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks of the Northern Pannonian Basin (Eastern-Central Europe): Geochemistry, Petrogenesis and Geodynamic Implications. Journal of Petrology, 42, 10, 1813-1843. Le Bas, M.J., Le Maitre, R.W., Streckeisen, A. & Zanettin, B., 1986: A Chemical Classification of Volcanic Rocks Based on the Total Alkali-Silica Diagram. Journal of Petrology, 27, 3, 745 – 750. Streckeisen, A., 1978: IUGS Subcommision on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks. Classification and nomenclature of volcanic rocks, lamprophyres, carbonatites and melilite rocks. Recommendations and suggestions. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie. Stuttgart. Abhandlungen. 143, 1-14.
Photomicrographs




Normative composition
Andesite is quartz – q normative rock, which, beyond common normative minerals, contains also normative diopside – di and hypersthene – hy. Garnet-bearing andesite from Šiatorská Bukovinka contains lesser amount of normative diopside and hypersthene compared to other andesites, what is likely caused by the fact that all Fe is listed as ferric iron Fe2O3. Andesite is not a corundum-normative c, rock.
Normative minerals
SiO2
TiO2
ZrO2
Al2O3
Fe2O3
FeO
MnO
MgO
CaO
Na2O
K2O
P2O5
F
S
CO2
Total
Molar proportion of normative mineral
Molecular mass of normative mineral
Weight % of normative mineral
Oxide
(wt. %)
61.62
0.56
17.65
6.43
0.00
0.15
2.03
6.09
3.18
2.03
0.18
99.92
Molecular
weight
60.08
79.88
101.96
159.69
71.85
70.94
40.31
56.08
61.98
94.20
141.95
Molecular
proportion
1.0256
0.0070
0.1731
0.0403
0.0021
0.0021
0.0504
0.1086
0.0513
0.0215
0.0013
ap
0.0042
0.0013
0.0013
328.68
0.42
il
0.0021
0.0021
0.0021
151.75
0.32
ru
0.0049
0.0049
79.9
0.39
or
0.1293
0.0215
0.0215
0.0215
556.67
12.00
ab
0.3078
0.0513
0.0513
0.0513
524.46
26.91
an
0.2005
0.1003
0.1003
0.1003
278.21
27.89
hm
0.0403
0.0403
159.69
6.43
zvyšky
0.0000
0.0504
0.0041
di
0.0082
0.0000
0.0041
0.0041
0.0041
216.56
0.89
hy
0.0462
0.0000
0.0462
0.0462
100.39
4.64
q
0.3336
0.3336
60.08
20.04
D: -0.3336
Mg/(Mg+Fe2+): 1.000
Total of normative wt. % 99.92
Comment Normative composition is calculated from the chemical composition expressed in wt. %, where all iron corresponds to Fe2O3. Hence, the norm contains only minor amount of ilmenite, whereas the residual molar proportion of Ti is affiliated to rutile – ru. Almost whole molar proportion of Fe3+ is affiliated with normative hematite – hm.
Chemical composition
Andesite is an intermediate sub-alkalic rock with SiO2 contents ranging between 57 and 63 wt. %, and Na2O + K2O contents around 5 wt. %. Intermediate rocks are also characterized by an increased CaO content compared to that in acidic rocks. Similar CaO contents (6 – 7 wt. %) are also typical for diorite – the plutonic equivalent of andesite. The andesite from Šiatorska Bukovinka is metaluminous, medium-potassic rock with A/CNK = 0.95 and A/NK = 2.38. The Mg/(Mg + Fe2+) ratio was recalculated after the conversion of all Fe2O3 to FeO. Trace element contents in andesites with garnets are similar to those without garnets. They only show a moderate enrichment in large lithophile elements (LILE – K, Rb, Cs, Sr, Ba), negative Nb anomaly and positive Pb anomaly pronounced in normalized records of trace elements. Such trends are typical for the magmas originating in subduction zones. Contents of rare earth elements La-Eu in garnet-bearing andesites are similar to those in garnet-free andesites. However, the garnet-bearing andesites are little depleted in heavy rare earth elements compared to the garnet-free andesites what probably reflects the garnet fractionation (Harangi et al., 2001).
-
SiO2
61.62TiO2
0.56Al2O3
17.65Fe2O3
6.43FeO
0.00MnO
0.15MgO
2.03CaO
6.09Na2O
3.18K2O
2.03P2O5
0.18LOI
0.99Total
100.91Mg(Mg/Fe2+)
0.38A/CNK
0.95A/NK
2.38