Nordmarkite
Category: Plutonic
Type Alkaline-feldspar syenite with quartz.
Commons A variety of the alkali feldspar syenite with quartz composed mainly of microperthite and acid plagioclase (oligoclase, albite), quartz (up to 7 vol. %), biotite (up to 5 vol. %), alkalic amphibole and /or alkalic pyroxene (up to 3 vol. %).
Name origin Nordmakite is named after the Nordmarka region near Oslo in Norway. The rock was mentioned for the first time by Brögger in 1890.
Locality Lake Mykle, Oslo graben, Norway (collection of Š. Dávidová).
GPS: 59° 25' 25,75" N, 9° 40' 38,44" E
Major minerals Microperthite, orthoclase, microcline, plagioclase, quartz, biotite.
Accessory minerals Ferro-eckermannite, aegirine, allanite, Ti-magnetite, apatite, pyrite, zircon, monazite, garnet.
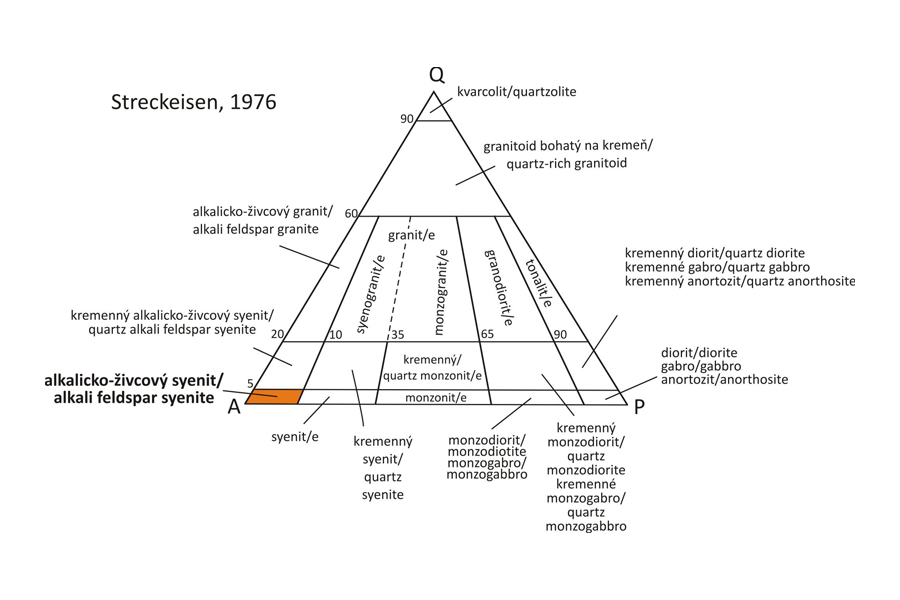
Classification According to modal composition, the field of alkali feldspar syenite is defined in the QAPF diagram for plutonic rocks (Streckeisen, 1976) by the modal content of quartz (Q 0-5 %) and the P/(P + A) ratio between 0 and 10.
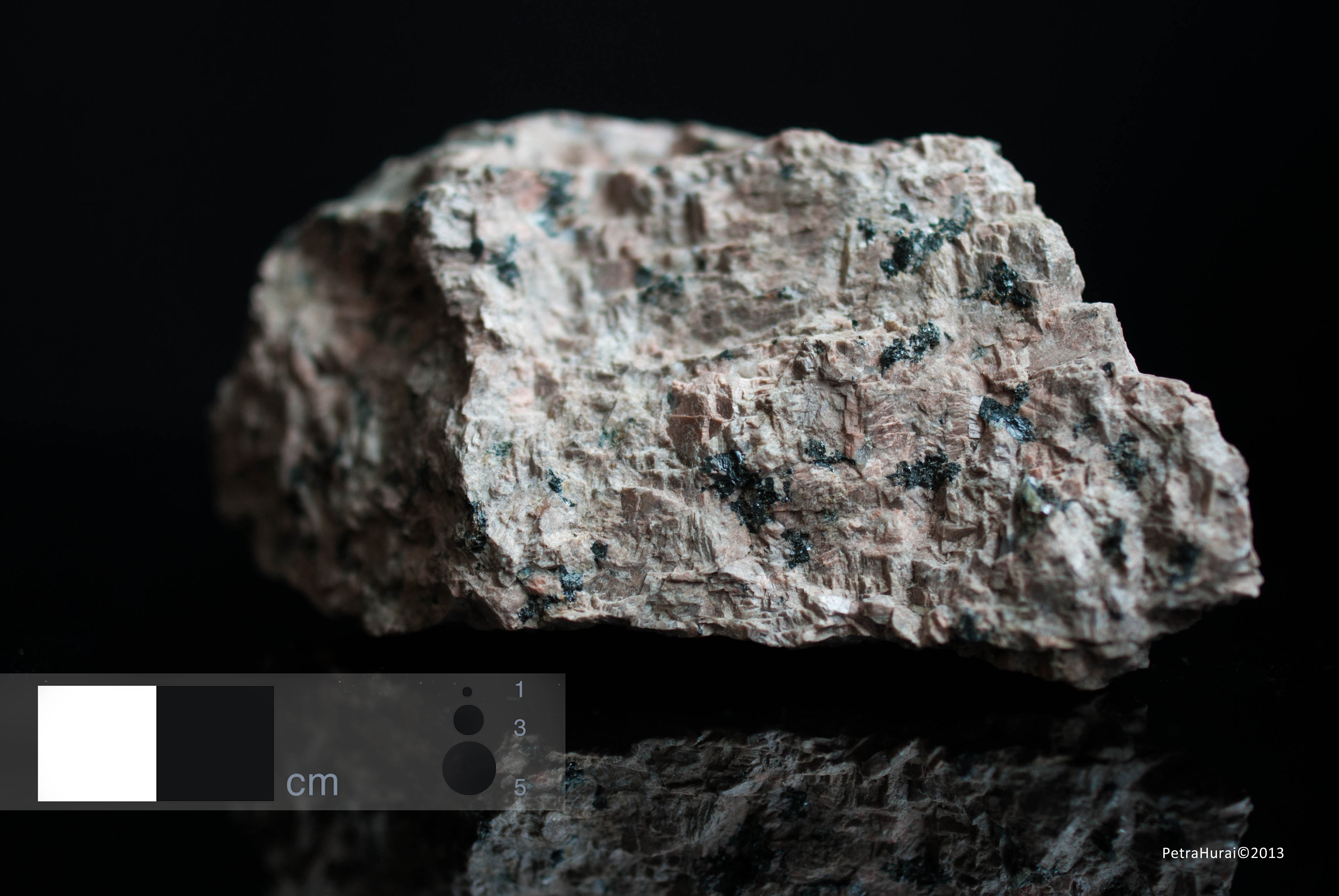

Colour Light pink rock with dark phenocrysts of biotite, pyroxene and/or amphibole.
Structure Massive, confined.
Granularity Coarse-grained rock.
Texture Holocrystalline, phaneritic, equigranular and hypautomorphic granular.
Alterations Alkaline feldspars are kaolinized in places.
Petrographic characteristics Alkaline feldspar is the dominant mineral of the coarse-grained alkaline feldspar syenite with quartz. The feldspar is intergrown with albite or another acid plagioclase, thus forming the microperthite. Quartz and mafic minerals – alkaline pyroxene and/or amphibole – occur in intergranular spaces between alkalic feldspars.
Usage Nordmarkite is used as a decorative cladding material.
Literature Andersen, T. & Sørensen, H., 2003: Mikrosyenite from Lake Mykle, Oslo Rift: Subvolcanic rocks transitional between larvikite and nordmarkite. Norges geologiske undersøkelse Bulletin, 441, 25-31. Daly, R.A., 1903: Geology of Ascutney Mountain, Vermont. Geological Survey Bulletin, 209, 7 – 212. Dietrich, R.V. & Heier, 1967: Differentiation of quartz-bearing syenite (nordmarkite) and riebeckitic-arfvedsonite granite (ekerite) of the Oslo Series. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 31, 2, 275-280. Knorring, O. & Dearney, R., 1960: A note on a nordmarkite and an associate rare-earth mineral from the Ben Loyal syenite complex, Sutherlandshire. Mineralogical Magazine 32, 383-391. Riishuus, M.S., Peate, D.W., Tegner, Ch., Wilson, J.R. & Brooks, K., 2008: Petrogenesis of Cogenetic Silica-Oversaturated and –Undersaturated Syenites by Periodic Recharge in a Crustally Contaminated Magma Chamber: the Kangerlussuaq Intrusion, East Greenland. Journal of Petrology, 49, 3, 493-522.
Photomicrographs
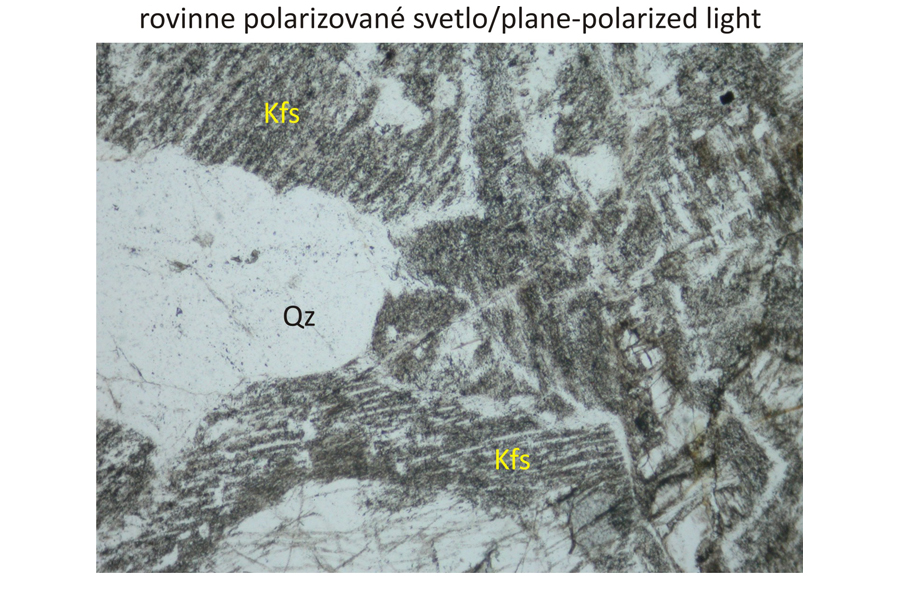

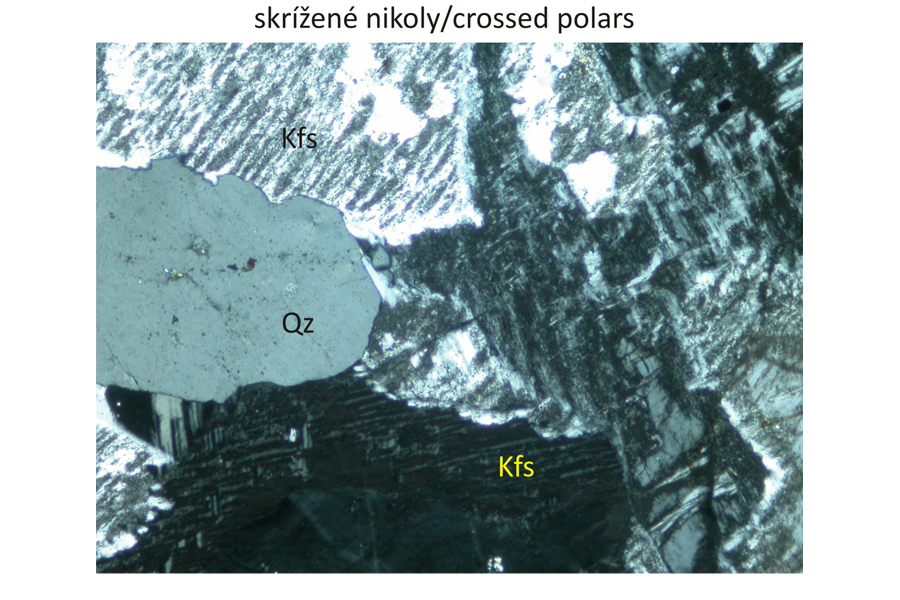
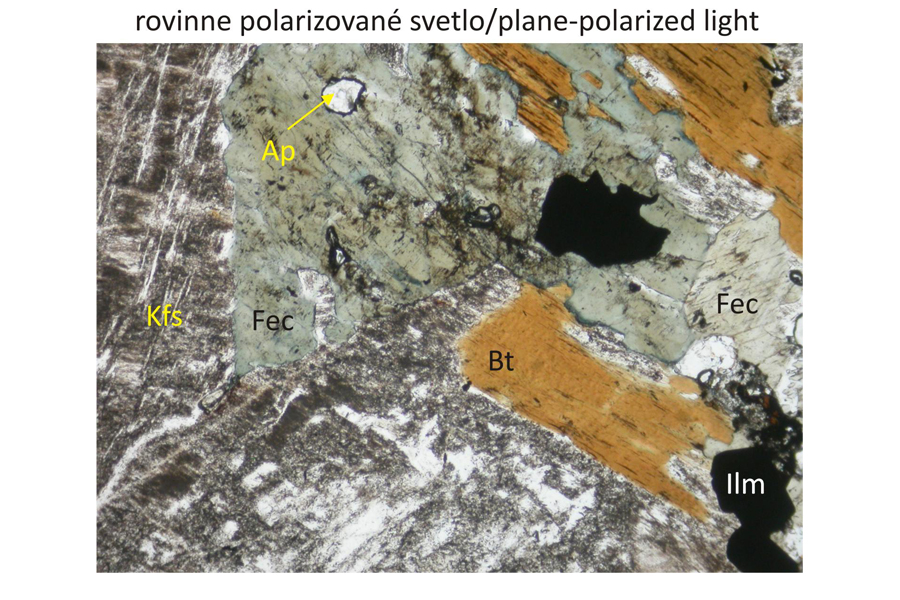
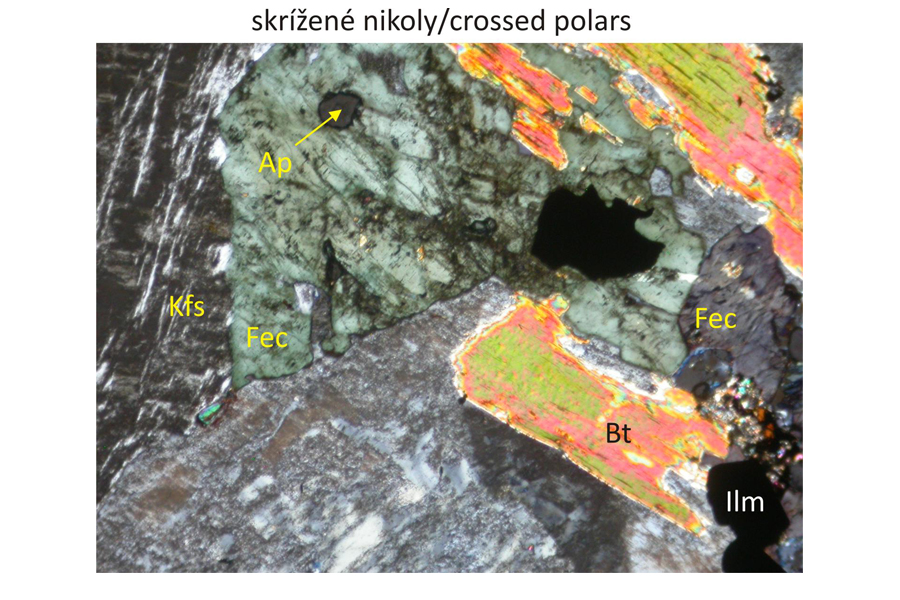
Potassium feldspar – Kfs intergrown with acid plagioclase, most frequently albite, and quartz – Qz. Exsolutions of acid plagioclases in form of tiny lenses, coarser lamellae or structures resembling tiny veinlets originated during slow cooling from initially homogeneous Na-K feldspars. These structures discernible in nordmarkites only under microscope are designated as microperthite. Potassium feldspar is in places replaced by a mixture of clay minerals originating at a low temperature (kaolinization). The alteration is discernible in plan-parallel polarized light as grey-coloured parts in the potassium feldspar. Biotite phenocrysts – Bt and alkalic amphibole – ferro-eckermannite – Fec – occur in intergranular spaces between alkali feldspars and quartz. Ferro-eckermannite displays faint blue-green to green-yellow pleochroism in plan-parallel polarized light. In contrast, another alkalic amphibole – arfvedsonite – has more intense blue-green, blue, violet to brown and brown-orange pleochroism. Fe-Ti oxides – Ti-magnetite or ilmenite – Ilm are opaque accessory phases. Bottom images also display accessoric apatite – Ap, in sections perpendicular to optical axis, that is in an extict position in crossed polars. Widths of all photomicrographs correspond to 2.2 mm.
Normative composition
Nordmarkite is quartz-normative rock with relatively high content of normative albite – ab and orthoclase - or. Depletion in CaO is reflected in a low content of normative anorthite – an. Some nordmarkites do not contain normative anorthite, but normative acmite – ac instead, and also hematite in the case of a Fe3+ excess. Nordmarkite, as a variety of alkali feldspar syenite with quartz, exhibits significantly increased content of normative quartz – q compared to that in common syenite.
Normative minerals
SiO2
TiO2
ZrO2
Al2O3
Fe2O3
FeO
MnO
MgO
CaO
Na2O
K2O
P2O5
F
S
CO2
Total
Molar proportion of normative mineral
Molecular mass of normative mineral
Weight % of normative mineral
Oxide
(wt. %)
60.80
1.27
15.83
2.40
3.45
0.15
1.31
2.29
5.05
5.33
0.42
98.30
Molecular
weight
60.08
79.88
101.96
159.69
71.85
70.94
40.31
56.08
61.98
94.20
141.95
Molecular
proportion
1.0120
0.0159
0.1553
0.0150
0.0501
0.0021
0.0325
0.0408
0.0815
0.0566
0.0030
ap
0.0099
0.0030
0.0030
328.68
0.97
il
0.0159
0.0159
0.0159
151.75
2.41
or
0.3395
0.0566
0.0566
0.0566
556.67
31.50
ab
0.4889
0.0815
0.0815
0.0815
524.46
42.73
an
0.0344
0.0172
0.0172
0.0172
278.21
4.78
mt
0.0150
0.0150
0.0150
231.54
3.48
zvyšky
0.0192
0.0325
di
0.0276
0.0051
0.0087
0.0138
0.0138
228.27
3.14
hy
0.0379
0.0141
0.0238
0.0379
112.10
4.25
q
0.0838
0.0838
60.08
4.31
D: -0.0838
Mg/(Mg+Fe2+): 0.629
Total of normative wt. % 98.30
Comment Normative anorthite – an was created from excess molar proportion of aluminium after creation of normative albite – ab and orthoclase – or.
Chemical composition
Normarkite is characteristic of increased SiO2 contents compared to those in syenite, ranging around 60 wt. %. It also has lower CaO and MgO contents. Contents of alkalis in syenite and nordmarkite are essentially similar, but that of K2O in nordmarkite is somewhat higher. F and Cl contents are negligible. The CO2 content is also low to negligible. The nordmarkite from the Lake Mykle is typical of increased Zr, Th, La and Ce contents compared to syenite.
-
SiO2
60.80TiO2
1.27Al2O3
15.83Fe2O3
2.40FeO
3.45MnO
0.15MgO
1.31CaO
2.29Na2O
5.05K2O
5.33P2O5
0.42H2O+
0.86Total
99.16Mg(Mg/Fe2+)
0.40A/CNK
0.87A/NK
1.12
-
SiO2
64.94TiO2
0.81Al2O3
16.25Fe2O3
1.68FeO
1.00MnO
0.06MgO
1.03CaO
1.56Na2O
6.08K2O
5.88P2O5
0.26H2O+
0.38H2O-
0.14Total
100.07Mg(Mg/Fe2+)
0.65A/CNK
0.85A/NK
0.99
-
SiO2
65.43TiO2
0.50Al2O3
16.11Fe2O3
1.15FeO
2.85MnO
0.23MgO
0.40CaO
1.49Na2O
5.00K2O
5.97P2O5
0.13H2O+
0.39H2O-
0.19F
0.08Cl
0.05Total
99.97Mg(Mg/Fe2+)
0.20A/CNK
0.93A/NK
1.10
-
SiO2
65.47TiO2
0.82Al2O3
14.91Fe2O3
2.10FeO
1.95MnO
0.23MgO
0.66CaO
1.23Na2O
6.58K2O
4.71P2O5
0.17LOI
0.19Total
98.83Mg(Mg/Fe2+)
0.38A/CNK
0.82A/NK
0.94